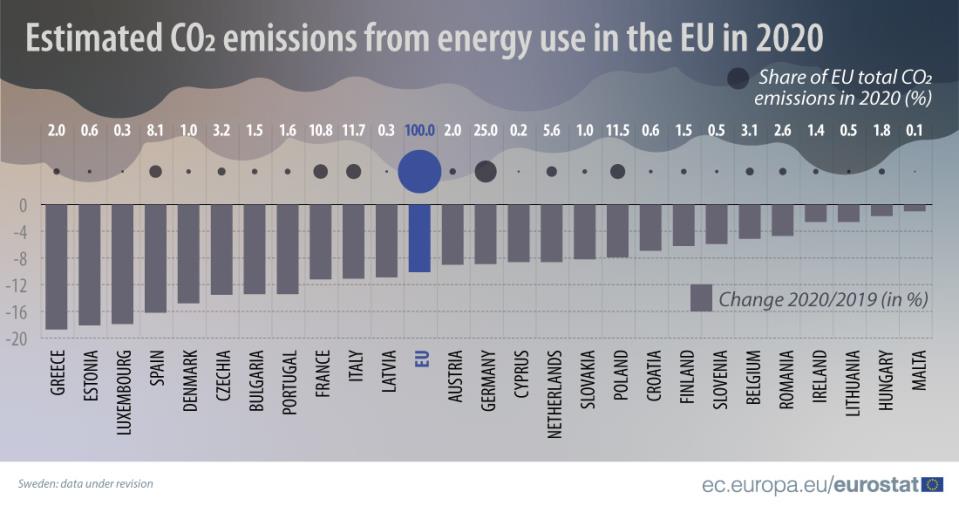
2020 saw a decrease in CO2 emissions from energy across every EU country when compared to 2019, Eurostat statistics reveal.
Eurostat estimates that in 2020, the year when Covid-19 containment measures were widely introduced by the EU Member States, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from fossil fuel combustion (mainly oil and oil products, coal, peat and natural gas) significantly decreased by 10% in the EU compared with the previous year. “CO2 emissions from energy use are a major contributor to global warming and account for some 75% of all man-made EU greenhouse gas emissions. They are influenced by factors such as climate conditions (e.g. cold / long winter or hot summer), economic growth, size of the population, transport and industrial activities.”
According to Eurostat estimates, emissions fell in 2020 in all EU Member States, with the largest decrease in Greece (-18.7%), followed by Estonia (-18.1%), Luxembourg (-17.9%), Spain (-16.2%) and Denmark (-14.8%).
The lowest decreases were seen in Malta (-1%), Hungary (-1.7%), Ireland and Lithuania (both -2.6%).
Eurostat explained that CO2 emissions from fossil fuels are generated in the country where the fuels are burned for purposes such as electricity generation, transport, steel production etc.
“Consequently, imports and exports of energy products have an impact: for example, if coal is imported for electricity generation this leads to an increase in emissions in the importing country, while if electricity as such is imported, it has no effect on emissions in the importing country, as these emissions would be reported in the exporting country where the electricity has been produced.”